Enable Cloud Transportation Management Service for BTP ABAP Environment
With the release 2302 in BTP ABAP Environment, it is now possible to integrate BTP ABAP software lifecycle management into Cloud Transport Management Service.
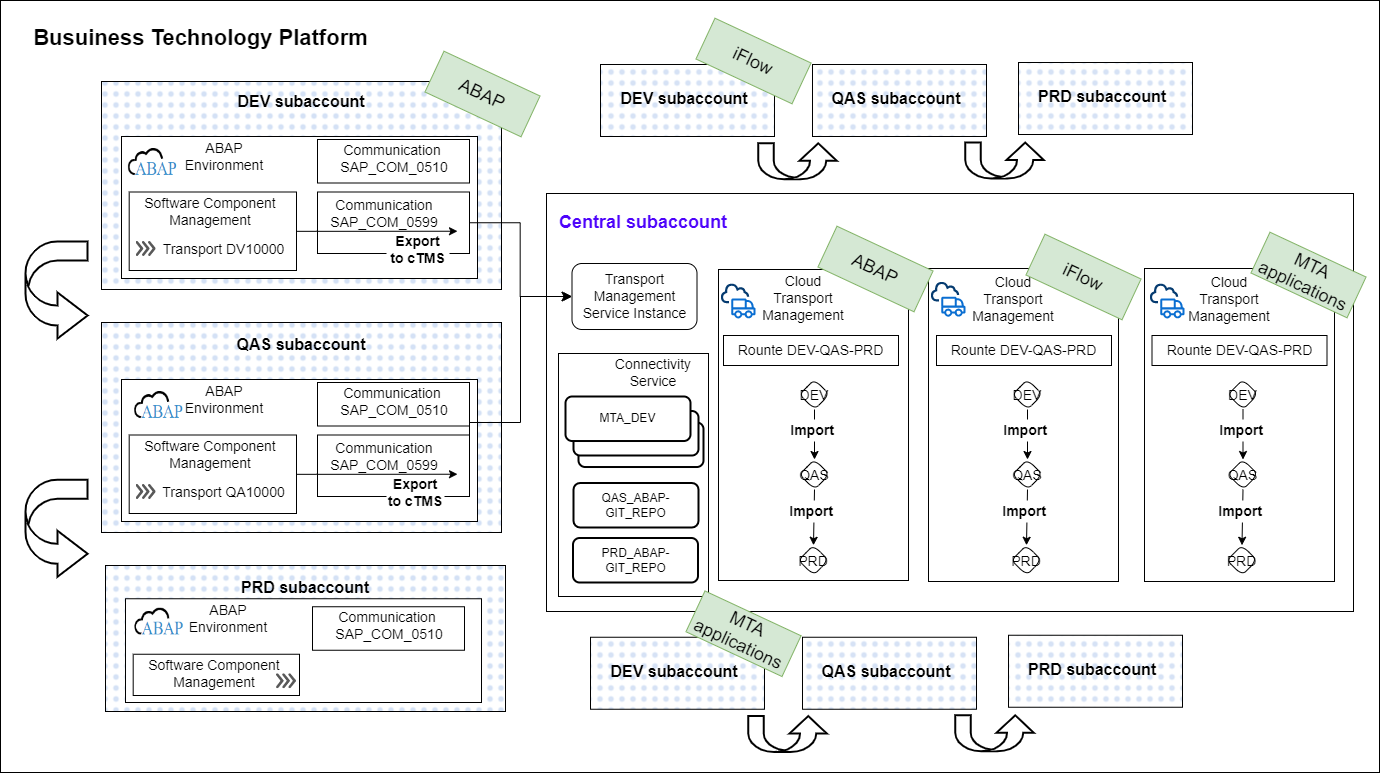
This blog starts with the concept of Centralized Cloud Transport Management and go into step-by-step setup to integrate BTP ABAP Environment into Cloud Transport Management.
Prerequisites:
- Cloud Transport Management Service
- BTP ABAP Environment
- Authorization to configure Destinations in BTP subaccount
Centralized Transport Management
SAP Cloud Transport Management Service(cTMS) lets you manage development objects and application specific artifacts across multiple subaccounts in BTP. It provides full visibility to what objects are transported from where to where, and the transport status and the logs. Its landscape wizard allows you to model complex landscape.
cTMS has been the core transport strategy for Integration development, such as transportation of integration flow artifacts, custom API in API management and other MTA content generated from Business Application Studio. Now, cTMS is able to handle content from BTP ABAP environment.
To translate this in a practicality, ideally, only one subaccount should run Cloud Transport Management Service(cTMS). If there is any other subaccount that runs cTMS, the effort will be redundant. Single cTMS can handle multiple transports routes across subaccounts in a single BTP global account. So it’s best to use a single subaccount and make it a central hub for controlling transport.
Existing transport mechanism for ABAP Environment
Before this integration with cTMS, what was the transport mechanism for BTP ABAP Environment? Actually, there were already two ways to manage ABAP objects transport between multiple subaccounts.
- Git-based CTS (gCTS)
- abapGit
Integration of cTMS into ABAP lifecycle management is a new feature, but not completely new. Rather, it’s an extension of Git-based CTS(gCTS). To perform transport with cTMS, we still have to use “Manage Software Components” app in the Fiori launchpad in ABAP Environment. This app has been the core function and interface for performing Git-based CTS(gCTS), and cTMS needs this app to trigger the export of transport request.
So in short, it’s not a new mechanism. Rather, it’s a better version of Git-based CTS(gCTS) where we can have much better control on transport inside Cloud Transport Management Service.

1. ABAP Environment
Configure Software Components
Before start developing any ABAP objects in the source system, we must define a software component. Go to Manage Software Components app from the Fiori Launchpad. Create a new software component. Choose Clone on the right top corner.

A pop up is prompted for you to configure the software component before the cloning. Enter the followings and clone.
| Branch to be checked out: | main |
| Repository Role: | Source Pull and Push |
| Options: | Latest |
After a few minutes, cloning should be finished and you can see in your ADT that the new package with the name of software component is created. Add to your favorite package.
Create a sub-package for development under that generated package. All the development objects should be under that sub-package. Create a test class and generate a transport request.

Configure outbound communication
In the source system, go to Communication System app and create a new system and name it “CTMS”. Enter the following parameters.
| Parameters | Value | Comment |
| Host Name | e.g. https://transport-service-app-backend.ts.cfapps.eu10.hana.ondemand.com | URI property in the service key created for cTMS. |
| Port | 443 | |
| Token Endpoint | <subdomain>.authentication.sap.hana.ondemand.com/oauth/token?grant_type=client_credentials | URL property in the service key created for cTMS. |
| Auth method | OAuth 2.0 | |
| OAuth 2.0 Client ID | <client ID from the service key> | Same service key |
| OAuth 2.0 Client Secret | <client secret from the service key> | Same service key |
Next, go to Communication Arrangements app and create a new arrangement from template SAP_COM_0599. Enter the following parameters.
| Parameters | Value | Comment |
| Communication System | CTMS | Communication system created on the previous step |
| CTMS Node Name | DEV-ABAP | Must match the transport node creaetd in cTMS |
| OAuth 2.0 Client ID | OAuth 2.0 user created in the previous step |

Configure software component test integration
In the source system, go to Maintain Communication Users app and create a new user.
Then go to Communication Systems app and create a new system. Use the user just created. In the host parameter, enter host URL of the ABAP environment. You can find it by right clicking the ABAP cloud project in ADT -> ABAP Development->System URL. Port is 443.
Finally create a communication arrangements app and create a new arrangement from template SAP_COM_0510. Use the communication user and system just created.

After the communication arrangement SAP_COM_0510 is created, a service URL is generated in the bottom of the page. This URL will be used in step 2 later.

Configure target ABAP Environment
In the target system, login to BTP ABAP Environment. This should be a different ABAP system that you want to use as target system where the development objects should be imported.
Follow the same previous step and Configure software component test integration in the target system. Note that it’s recommended to use different user password, and be aware that the host URL for ABAP system should be different from the source system.
Clone software component in target ABAP Environment
As a result of the first step when you created software component, there should be the same software component created in the ABAP Environment in the target subaccount. Access the Manage Software Component app and the “Cloned” status should be “No”. Go ahead an choose clone and follow the same steps as we created software component in the first step. The software component package will be generated in your target system as well, once the cloning is complete.
2. Configure Destinations
Go to the subaccount where Cloud Transport Management Service is created. Create a new destination that points to ABAP environment source system.
| Parameters | Value |
| Name | DST_DEV_ABAP(name of your choice) |
| Type | HTTP |
| URL | Service URL created in ‘Configure software component test integration‘ section |
| Proxy Type | Internet |
| Authentication | BasicAuthentication |
| User/Password | User Password created in step ‘Configure software component test integration‘ section |
Go on and create a new destination that points to ABAP environment target system.
| Parameters | Value |
| Name | DST_QAS_ABAP(name of your choice) |
| Type | HTTP |
| URL | Service URL created in ‘Configure target ABAP Environment‘ section |
| Proxy Type | Internet |
| Authentication | BasicAuthentication |
| User/Password | User Password created in ‘Configure target ABAP Environment‘ section |
Do connection check and both connection should return 200 OK.

3. Cloud Transport Management Service
Create source & target system nodes that refers to source & target ABAP system.

| Parameters | Value | Comment |
| Name | DEV-ABAP / QAS-ABAP | |
| Allow upload to Node | X | Allows manual upload of transport file |
| Forward Mode | Auto | Auto = transport automatically transferred to target node defined in the route. Manual = transport request will NOT be forwarded to target node for import. Instead, user must manually forward it. |
| Content Type | BTP ABAP | |
| Destination | <Your destination created in step 2> | |
| Deployment Strategy | default | Only “default” is available for content “BTP ABAP”. Default strategy = the old version of object in target system will be stopped before the deployment of new version. Blue-Green strategy = Import objects replace the old version in the target system without downtime. |
Create transport route connecting these two nodes.

4. Transporting ABAP objects
Go to ADT and the transport request created in the first step and release it. Go to Software Lifecycle Management app and in the main branch, there is an update that shows your transport request has been committed. Check on the commit with the transport request number and choose Export to Cloud Transport management Service. A pop up is displayed for you to select node for export. Select the source system node configured in first step in ABAP Environment.



Now go to Cloud Transportation Management Service and go to Transport Action Logs from left side pane. You should be able to see that your commit ID with the transport request is exported from the source node.

Next, go to the target node. The transport request ID should be ready to be imported to the target system. Choose Imported Selected and approve the pop up.

Check the transport action log. The importing process should be logged with overall status. Click on the row and you can see the detailed import log as well. In case of import errors, detailed transport log will help you what went wrong during the importing process.


As the result of this import, you should be able to find the ABAP class object created in 1.1 transported to your target system.